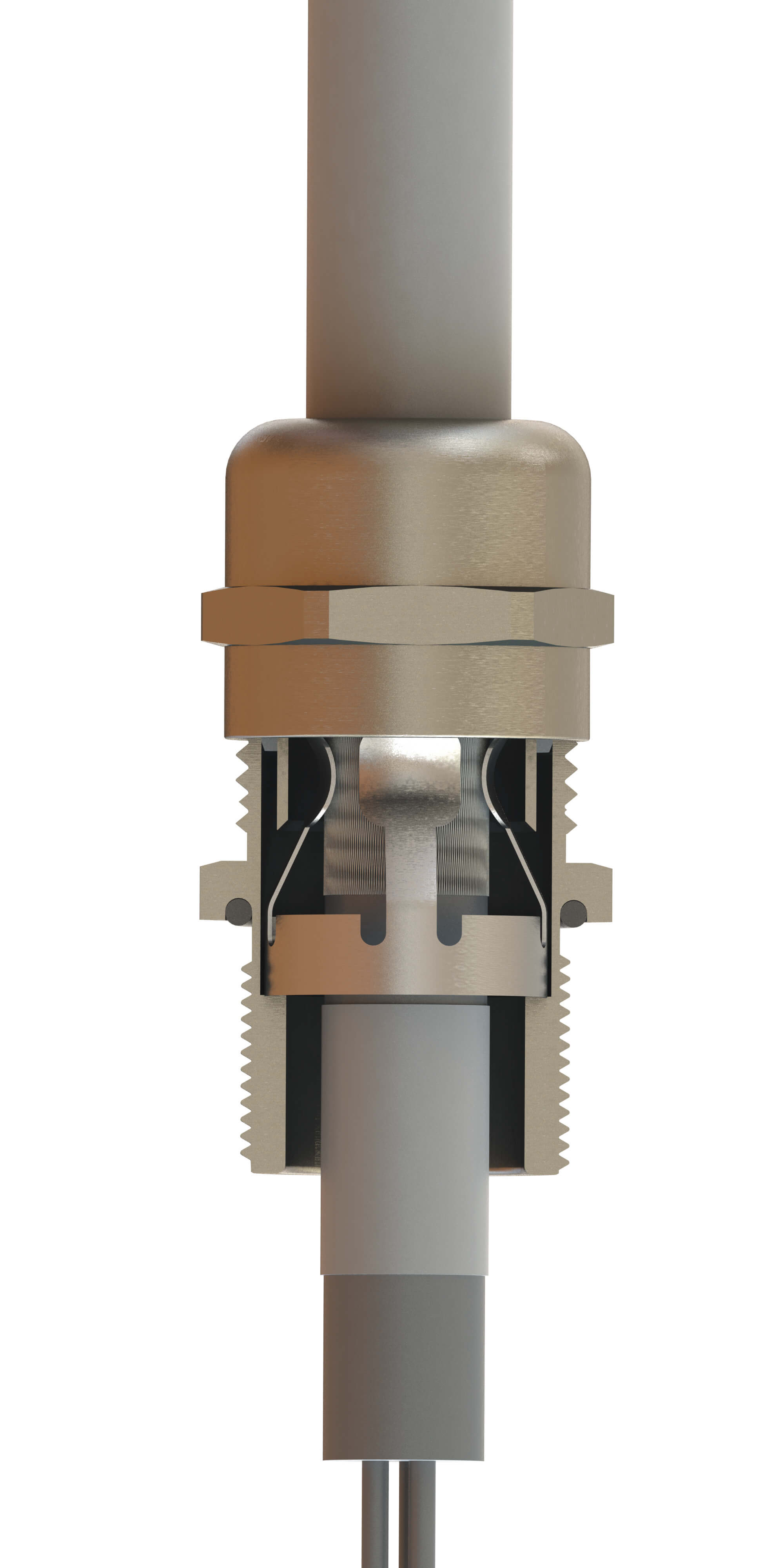
Cable glands are indispensable for protecting wire and cable terminations against unwanted disconnections or damage in machines and control cabinets. Because different cable glands accommodate different cables, materials or application needs, choosing the right one can be difficult. This blog will cover various cable glands and their benefits so you may choose the best one for your application. As you begin, be sure to identify the following factors during the selection process:
- The type of cable being used. Each cable type presents a different requirement. For instance, flex cables can prove versatile where constant, repeated motion occurs, and certain cable glands can help protect them from inherent conductor fatigue. Another example — VFD and shielded cables — need cable glands that create a ground path to earth ground for EMC protection. And several smaller cables sharing a common termination point require a cable gland with multiple holes.
- Cable diameter. The cable diameter will determine the gland’s hole diameter for proper cable feedthrough.
- The application’s environment. Certain cable glands protect against specific threats such as dust, vapors and liquid exposure or submersion, extreme temperatures, vibrations, impacts and explosion.
- Material requirements. Material selection factors into how well your termination stands up to its environment and how well your gland works with your cable’s material.
- Approvals. Some extreme environments — especially those where human safety is critical — require approvals from a specific standards organization as well as local approval. Cable glands may require UL 94V-2 flammability rating, IP 68 ingress protection against dust and immersion, or approvals indicating explosion protection. Cable glands should also carry UR, cUR, UL and CSA marks for use in the United States and Canada.
There’s a Cable Gland That Meets Your Needs.
Once you identify your cable type, diameter, materials and approval requirements, you can better align your needs with a suitable cable gland. SAB North America offers an expansive offering of cable glands made from a wide range of materials — including Polyamide 6, nickel-plated brass and stainless steel — and carrying relevant approvals so they can be used with power, control and data cables across many industries. Some of the most popular cable gland types include:
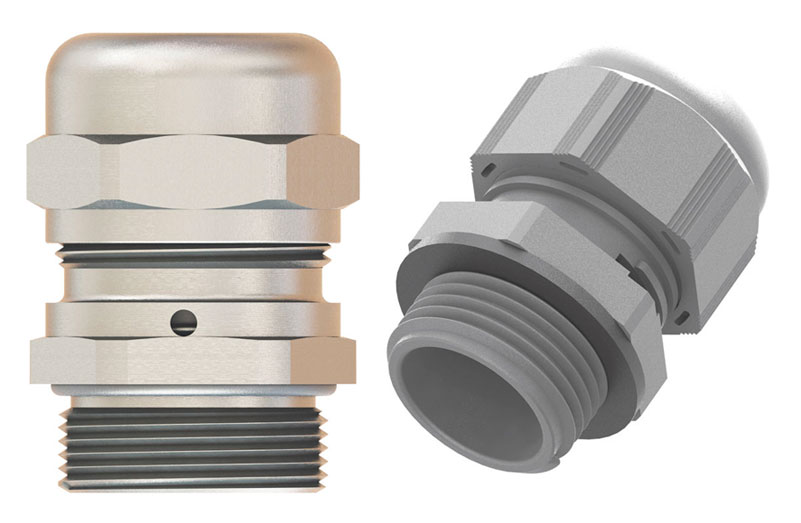
- Standard glands. Constructed of Polyamide 6, nickel-plated brass, or stainless steel, these multi-purpose glands include versions that provide a liquid-tight seal, corrosion and impact resistance, or strain relief offering maximum protection against conductor fatigue caused by flexing cables. Available with NPT, PG or metric threads.
- EMC glands. Glands such as SAB EMC-2 and EMC-4 offer built-in grounding mechanisms that come in contact with a cable shield to create a ground path to earth ground along with impact and vibration resistance. Available with NPT, PG or metric threads.
- Vent glands. SAB’s vent glands are used to secure a cable and balance the pressure in an enclosure to protect connections from condensation. Available with PG or metric threads and constructed of nickel plated brass or Polyamide 6.
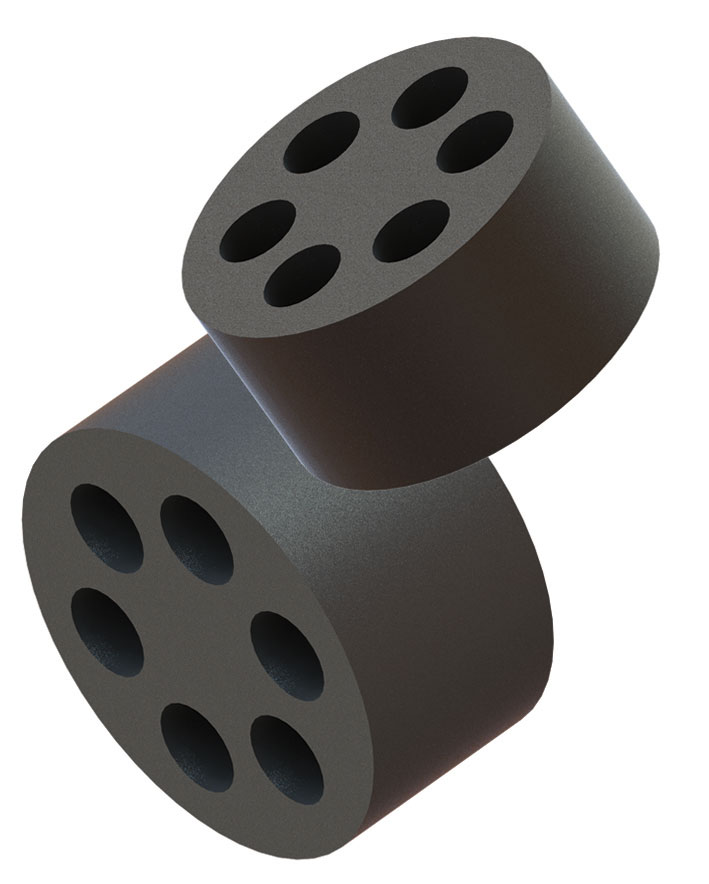
- Multi-hole bushings are desirable when there is limited space on a control cabinet or when multiple smaller cables need to be secured. They can be used with a SAB cord grip for an exceptional seal.
Careful attention to criteria such as cable type and diameter, materials and approvals will go a long way toward determining the right gland for your termination. SAB North America has a cable gland that will meet your cable, material, grounding and industry requirements so you'll gain optimal protection for your terminations.
To purchase SAB North America cable glands, visit our online store. Or, for more information, download our brochure.